Computer evolution is usually categorized into five generations. The first generation (1940-1956) are known as vacuum tubes, second generation (1956-1963), called transistors, integrated circuits (ICS), called third generation (1964-1971), and fourth generation (1971), called microprocessors. Finally, the fifth generation that exists is called artificial intelligence (AI). Each generation has significantly improved in size, speed, reliability and cost.
These different generations of computers were useful and gradually became smaller, faster, more efficient and more powerful. It also provided a more user-friendly interface and a wider connectivity. Each generation is built on previous generations, leading to advances that have changed many aspects of life and work. Previous computers were limited in functionality, but over time, progression has reached its peak with the personal computers we use today, becoming smaller, faster, and more powerful computers. This article provides a detailed explanation of the generation of computers and their evolution. So keep reading and learn more.
Five generations of computers and their evolution
Computer evolution can be summarised as progression from a larger, slower, less reliable machine to a smaller, faster, more powerful device. The invention of vacuum tubes, transistors, integrated circuits, and microprocessors has dramatically improved size, speed and efficiency, respectively. However, modern computers featuring artificial intelligence, machine learning and quantum computing represent the greatest stages of this ongoing evolution.
Here are 5 generation computers in detail.
First Generation Computer (1940-1956) – Vacuum Tube
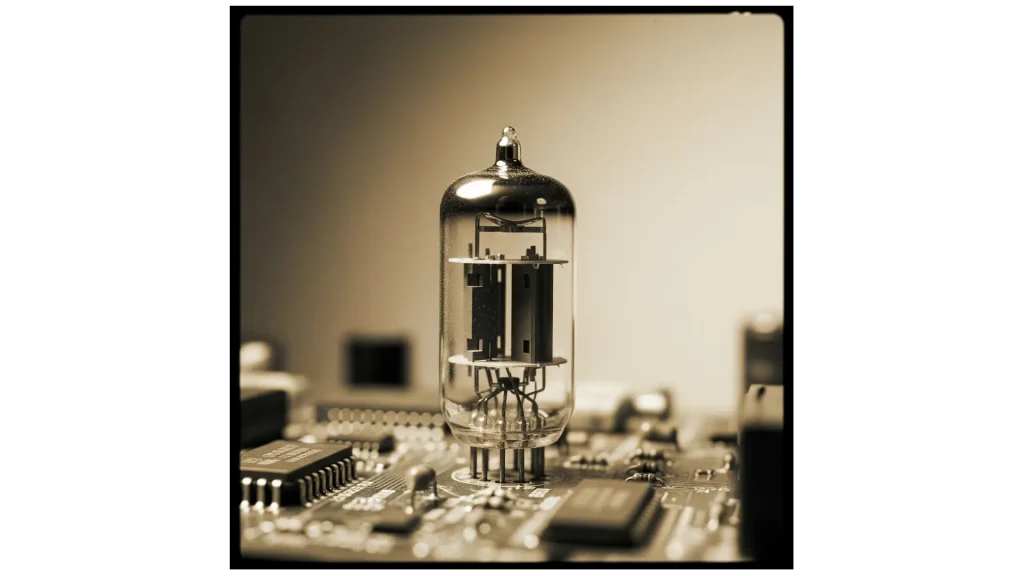


- As for that technology, vacuum tubes were the core components of switching and amplification.
- It was large and consumed a lot of electricity. As a result, it produced quite a lot of heat, was slow and very expensive.
- Programming – Machine Language (low level).
- Some of these examples are Eniac and Univac.
- It was mainly used for scientific calculations and military applications.
Second Generation Computer (1956-1963) – Transistor

- The transistors have been replaced with vacuum tubes, making them smaller in size and less power consumption.
- Its main feature is that it is smaller, faster and more reliable than first-generation computers.
- Programming – Assembly Language and high-level languages such as Fortran and Cobol.
- Examples include the IBM 7000 series and the Univac 1170.
- It was used for business data processing and scientific research.
- The second generation made the computers more accessible and affordable, but they were still bulky and expensive.
Third Generation Computer (1964-1971) – Integrated Circuit (ICS)

- Integrated Circuits (ICS) combine multiple transistors on a single semiconductor chip.
- Multiple transistors were created on a single silicon wafer, further reducing the computer.
- It’s smaller, faster, more reliable and affordable than previous generations. It also enabled the development of operating systems and multitasking.
- Programming – High-level languages and operating systems.
- Examples include IBM System/360 and PDP-8.
- It has been expanded to include business applications, multitasking, and real-time processing.
- With increased accessibility and affordability, businesses and organizations have had wider adoption.
4th Generation Computer (1971-present) – Microprocessor

- The invention of microprocessors (a single chip containing a CPU) revolutionized computing.
- It’s smaller, more powerful and more affordable than ever. Personal computers are also widely available.
- Programming – A wide range of programming languages and operating systems, including user-friendly graphical interfaces.
- Used for personal computing, the Internet, entertainment and multimedia.
- Fourth generation computers have changed how people function, communicated and accessed, through the development of software applications for a variety of purposes.
5th Generation Computers (Current and Later) – Artificial Intelligence (AI)


- The fifth generation of computers focuses on AI technology, natural language processing and parallel processing.
- Its characteristics include continuous miniaturization, increased processing power, and the development of more intelligent and intuitive systems.
- It focuses on parallel processing, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
- Examples include AI-driven systems, advanced computing, cloud computing, and robotics.
- Can be used for advanced AI tasks, big data analytics, cloud computing, and robotics.
- The fifth generation of computers has brought advances in a variety of fields, including transportation, healthcare, and automation, and AI plays a major role in many aspects of modern life.
Conclusion
Computer evolution is usually divided into five generations, each characterized by significant technological advances. The first generation computer (1940-1956) used vacuum tubes, while the second generation computer (1956-1963) used transistors. The third generation computer (1964-1971) saw the introduction of integrated circuits, while the fourth generation computer (1971) brought microprocessors. For the fifth generation, they are characterized by artificial intelligence and parallel processing.
Each generation of computers brings significant advances in size, speed, capacity and cost. The evolution from vacuum tubes to transistors, integrated circuits and microprocessors has dramatically changed the computing landscape. Understand that fifth generation computers are still under development and research is underway on AI, quantum computing, and other advanced technologies. Therefore, we can expect exciting new features and advancements in the future. It is believed to provide a more immersive experience, enhancements on existing devices, and a shift towards personalized and intuitive interactions with technology.





